
WHAT IS PHYSICAL SELF?
Physical Self refers to the body, this marvelous holder and complex, finely tuned, machine with which we interface with our environment and individual creatures. The Physical Self is the concrete measurement, the unmistakable perspective of the individual that can be straightforwardly watched and inspected.
In Psychoanalytical school, Sigmund Freud’s construction of self and personality makes the physical body the core of human experience. Freud was of the view that the ego is first and foremost a body ego (Freud, 1937). However, in spite of Freud’s recognition of the centrality of body, his own writings on therapy rarely discuss it. Among western theorists Wilhelm Reich seems to probably most concerned with body (Fadiman and Frager, 2002). Although, in his later works, Freud placed less emphasis on libido, Reich took Freud’s concept of libido as his central principle. For Reich, the freeing of the blocked bioenergy is the chief task of psychotherapy. Reich argued that mind and body are one; all psychological processes, he postulated, are a part of physical processes, and vice versa. So for Reich, body is essential dynamic in all psychological functioning and it plays a critical role in storing and channeling the bioenergy, which is the basis of human existence and experience.
For Erik Erikson, experience is anchored in the ground-plan of body (Erikson, 1963). According to him the role of bodily organs is especially important in early developmental stages of a person life. Later in life, the development of physical as well as intellectual skills help determine whether the individual will achieve a sense of competence and ability to choose demanding roles in a complex society. For example, healthy children derive a sense of competence as their bodies become larger, stronger, faster and more capable of learning complex skills. However, as a stage theorist, Erikson is aware of the constant interaction of the body, psychological processes and social forces. He acknowledges the classical Freudian view of fundamental biological drives but insists that these drives are socially modifiable. Self-concept is made up of one’s self-schemas, and interatomic with self-esteem, self-knowledge, and the social self to make the self as a entirety. It incorporates the past, show, and future selves, where future selves speak to individuals’ thoughts of what they might ended up, what they would like to gotten to be, or what they are anxious of getting to be. Conceivable selves may work as motivating forces for certain conduct.
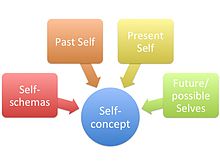
The discernment individuals have around their past or future selves relates to their discernment of their current selves. The worldly self-appraisal hypothesis contends that individuals have an inclination to preserve a positive self-evaluation by removing themselves from their negative self and paying more consideration to their positive one. In expansion, individuals have a propensity to see the past selfless positively (e.g. “I’m superior than I used to be”) and long-term self more emphatically (e.g. “I will be way better than I am presently”).

Physical characteristics are defining traits or features about your body. These are aspects that are visually apparent, knowing nothing else about the person. The first thing you see when you look someone could be their hair, clothes, nose, or figure. These are all examples of physical characteristics. To get good examples of physical characteristics you should look at a person’s face, how tall they are, and what they are wearing.
“HOW CAN I GROW AS A PERSON, IN CONTEXT OF PHYSICAL SELF”
Physical self. This aspect is much relatable to me as a woman because there is a time that I envy the other woman and I sometimes compare my physical body or self to others because of their natural beauty. I envy to their beauty and the way they carry themselves but the time pass by, I learn to love myself and thought myself that everyone of us, humans, is different to each other and there’s nothing to be ashamed of because everyone of us had this unique beauty. Just accept what is yours and love this and be confident of it and that the time the body possitivity come in. Body positivity refers to the declaration that all individuals merit to have a positive body picture, in any case of how society and prevalent culture see perfect shape, estimate, and appearance. It also too points to assist individuals get it how well known media messages contribute to the relationship that individuals have with their bodies, counting how they feel almost nourishment, work out, clothing, wellbeing, character, and self-care. By superior understanding the impact that such impacts have, the trust is that individuals can create a more beneficial and more practical relationship with their bodies.
Body inspiration is outlined to cultivate acknowledgment and adore of your body, but it can be a battle that includes another component of weight and incomprehensible guidelines to live up to. The body inspiration message is that you just ought to alter how you are feeling almost your body, but can moreover be fair one more request.
What is Sexual Self?
This is a part of yourself where you learn and understand your sexual development and how people’s sexual activity, beliefs, misconceptions and unlimited access from the internet on sex can influence your own sexual behaviors and responses.
Sexual self-concept defined as an individual’s assessment of his or her claim sexual sentiments and actions is proposed as an imperative indicator of prophylactic behavior among youngsters, and a scale measuring the concept is portrayed.
Sexuality frequently refers to a person’s sexual introduction or inclination. Your sexual introduction is who you’re sincerely, rationally, and physically pulled in to. Sexuality can moreover allude to a person’s capacity for sexual sentiments. More than the have to be replicate, sexual drive is an critical portion of human enthusiastic expression and profound connection with another. It’s not clear whether our sexuality could be a result of hereditary or hormonal components, our childhood and child rearing, or the society and culture we develop up in.
Sexual self-concept refers to the totality of oneself as a sexual being, including positive and negative concepts and feelings. According to theorists, sexual self-concept is described well along three dimensions (Snell & Papini, 1989): sexual self-esteem, sexual depression, and sexual preoccupation.
Because attachment style moderates one’s sense-of-self in general and one’s expectations about and strategies for approaching relationships, sexual self-concept may be a good indicator of what kinds of relationships we tend to get into, and how we tend to behave within relationships, with an emphasis on sexual satisfaction.
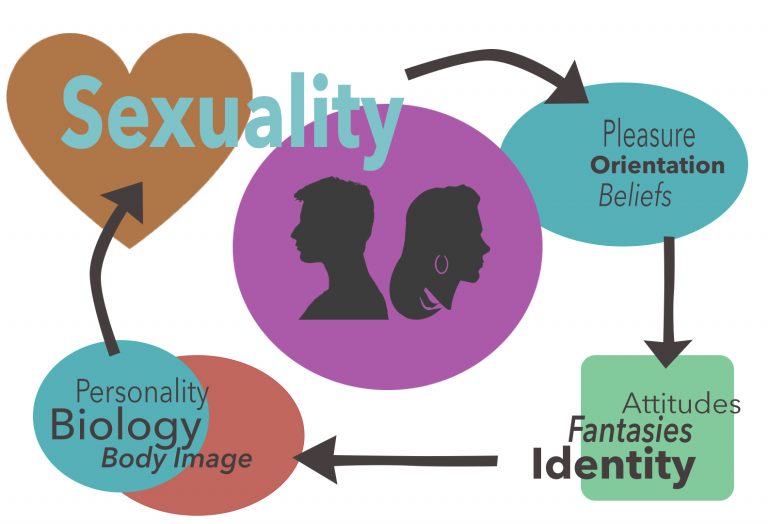
Creating a Sexual Self
*Sexual self-esteem – perception of their worth as sexual beings
*Sexual self-efficacy – perception of control over sexual experiences
*Sexual self-image – beliefs about sexual need
FOUR SEXUAL STYLES
*Sexually naive- have little confidence in sexual attractiveness, feel no control over sexual situations
*Sexually unassured- low self-esteem and little sense of control in sexual encounters, but interested in exploring their sexuality
*Sexually competent- confident of sex appeal and ability to control sexual situations, interested in exploring their sexuality and were sexually experienced
*Sexually driven- similar to above style, unable to say no to sex, mostly boys
PROTECTIVE FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH DELAY OF SEXUAL ACTIVITY
*Biological- late maturation, being female, intelligence
*Psychological- strong religious beliefs, involvement in school
*Social- parental monitoring, family religious beliefs, not dating steadily, not using alcohol or drugs.
“HOW CAN I GROW AS A PERSON, IN CONTEXT OF SEXUAL SELF”
Developing a sexual self is an important developmental task of adolescence. Your sexuality can play an important role in your identity and sense of self. Sexuality frequently alludes to a person’s sexual introduction or inclination. Your sexual introduction is who you’re sincerely, rationally, and physically pulled in to. Sexuality can moreover allude to a person’s capacity for sexual sentiments. More than the have to be replicate, sexual drive is an critical portion of human enthusiastic expression and profound connection with another. It’s not clear whether our sexuality could be a result of hereditary or hormonal components, our childhood and child rearing, or the society and culture we develop up in. In any case, investigating your sexuality is ordinary, sound, and profoundly individual.
Your sexuality is central to your self-identity, and not being able to express this is damaging to your sense of self-worth and overall mental health.
Sexuality is an important part of who you are. There is no right or wrong, it’s about what’s right for you.
A few individuals have a difficult time tolerating others who are diverse to themselves. On the off chance that somebody gives you a difficult time around your sexuality, it’s great to conversation to somebody approximately it. You don’t got to bargain with it by yourself.

What is Emotional Self?
Emotional Self-Awareness is the capacity to get it your claim feelings and their impacts on your execution. You know what you’re feeling and why—and how it makes a difference or hurts what you’re attempting to do. You sense how others see you and so adjust your self-image with a bigger reality. You’ve got an exact sense of your qualities and impediments, which gives you a realistic self-confidence. It too gives you clarity on your values and sense of reason, so you’ll be more definitive after you set a course of activity.
Emotional self-regulation or emotion control is the capacity to reply to the continuous requests of involvement with the run of emotions in a way that’s socially mediocre and adequately adaptable to allow unconstrained responses as well as the capacity to delay unconstrained responses as needed. It can too be characterized as outward and natural forms dependable for checking, assessing, and altering enthusiastic reactions. Enthusiastic self-regulation has a place to the broader set of feeling direction forms, which incorporates both the direction of one’s claim sentiments and the control of other people’s feelings.
5 Ways to Take Care of Yourself Emotionally
1. Know your emotions.
All of them. What are your past experiences with each emotion? Know what triggers each of them. Understand which events, and especially people, are associated with each. Do you understand why you respond emotionally the way you do? Are you satisfied that your emotional response is appropriate and reflects what you truly feel? Or, does your emotional response feel uncomfortable — for example, over reactive (or not reactive enough for the situation)? Do you feel frustrated that you can’t adequately express yourself?
Knowing your emotions should help you judge how to behave when a situation arises. Each new event or interaction should not feel like the first time it’s happening. Each successive time a specific emotion is expressed gives you another opportunity to observe yourself and respond in a way that feels right (or at least better) for you.
2. Maintain healthy boundaries.
Think of a boundary as a healthy space around you. You decide how big this space needs to be for you to feel comfortable. It may be an actual space, measured as physical distance, or an imaginary psychological/emotional space. When you successfully maintain healthy emotional boundaries, you are taking care of yourself first and foremost. Once you’ve done that, you can actually deal with a situation or person more effectively, since you know what you can and will do, as well as what you will not allow to happen emotionally.
3. Cultivate your own well-being on every level.
Practice self-care whenever possible. Physical care will keep you healthy and strong, better able to endure life when difficult things happen. Psychological well-being goes a long way to help sustain you, especially during life challenges when you are called upon to emotionally respond. Understanding who you are at your core, what makes you tick, how you differ from or are similar to those around you, and what your attitudes and beliefs are will help keep you on the “right track,” able to stay on your path in order to accomplish what you desire. As with emotions, your psychological outlook helps keep you steady in your own life.
4. Create a healthy support system.
These are people who encourage and nurture you. These are people who know you, like who you are, and are willing to help you become your best self. People with no ulterior motive or private agenda. These are people you can always turn to just to listen and/or provide advice if needed.
5. Create an emotional or psychological “toolbox.”
This is a great visual for many of these concepts. Your “toolbox” is a place where you keep your coping skills — life management tools that you have acquired over time and over the course of having had numerous life experiences. These tools are strategies you have developed and used effectively to cope with challenges to your life and well-being.
Over time, your personal “toolbox” should come to contain everything you need. My patients know they have the tools to deal with most of what life dishes up, and they feel confident that when a challenge occurs in the future, they have what it takes to handle it. In challenging times, however, people may feel that they need to seek help in order to gain a broader perspective, and perhaps add more strategies in order to better deal with a certain situation. Anything that helps you to grow emotionally and become more grounded within yourself is always a welcome addition to your life.

“HOW CAN I GROW AS A PERSON, IN CONTEXT OF EMOTIONAL SELF”
As a person, we must know our emotion and we must aware of our emotion in order to react properly to the situation that might happen. You grow as a person in context of emotional self by increasing your emotional intelligence. A lot of people might not truly know their emotional self that is why sometimes they react wrongly to the things that happens. Emotional intelligence is the skill of to be aware of, control and ultimately express emotions. It also teaches how to identify your emotions and be aware of them, their triggers and their impact. In order you to grow in the context of emotional you must identify your triggers. A trigger is a person, a situation or a condition that makes your emotional and prompts you to certain actions. Identifying your trigger leads you to improved your emotional intelligence, because it would allow you to develop the ability to control the outcome. It could give you the skill to calm down, take control of your actions and maintain your presence of spirit.in order to do that you must find the specific cases and start generalizing from there. If you understand what your pushes buttons, that would make the situations more manageable because the emotions will not come as a surprise. Most people go through their lives without paying attention to their emotions. Either completely ignoring them, r letting them control their lives. Emotions are a powerful force that can do miracles with your life, or completely ruin them. It is the job of your mind to learn to spot them and put itself between the emotion and the physical reaction. By learning that skill, you would finally be able to get reins of your life in your own hands.